How does content appear in search results? Why do search engines rank your competitors’ websites higher than yours?
To find the answers to these questions, you need to start with SERP analysis.
But what is SERP analysis?
In this article, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about this strategy and show you how to use it effectively to improve your website’s search rankings.
What is SERP Analysis?
Before anything, let’s start understanding what SERP is.
A search engine results page (SERP) is the page you see after typing a query into Google. SERP analysis is the process of examining what’s already ranking on Google. By analyzing the top-performing pages, you can discover what works, what doesn’t, and make smarter decisions to improve your SEO rankings.
Having this information at your hands, you can provide more value to users and probably outrank your competitors.
Why Should You Do SERP Analysis?
If you invest enough time in doing SERP analysis, it can benefit your keyword research and content creation processes.
Here is why it’s also beneficial:
- Understanding search intent
You will see what users actually want when they search for a keyword and what type of content ranks for it.
- Checking ranking difficulty
SERP analysis allows you to check how strong the competition is and to figure out how hard it will be to rank for certain keywords.
- Uncovering competitor strategies
Through SERP analysis, you will learn what top-ranking pages are doing right so you can apply similar strategies to your content.
- Identifying content gaps
And finally, you will be able to find what the existing top content is missing so you can create better content that fills those gaps.
In short, analyzing the SERP is important for understanding what Google likes for specific searches and how to position your content well.
How to Analyze a Google SERP in 5 Steps
Now that you understand the reasons and benefits behind a SERP analysis, you may be wondering how to carry it out effectively.
Here is how to perform a complete SERP analysis using five key steps:
1.Understand Search Intent
Search intent is the real reason behind a user’s query. Here, Google is good at matching results to what users actually want to find.
The four main types of search intent are:
- Informational: Users looking for knowledge or answers (e.g., “what is keyword research”)
- Navigational: Users looking for a specific website or page (e.g., “Google Search Console login”)
- Commercial: Users checking out products before buying (e.g., “best SEO tools 2026”)
- Transactional: Users ready to take action or buy (e.g., “buy Ahrefs subscription”)
Here’s how to identify search intent:
- Do a simple Google search.
- Then, look at the types of pages ranking on the SERP. If you see mostly blog posts and guides, the intent is informational. If product pages and online stores lead, it’s transactional.
The content format and style of top-ranking pages show what Google thinks users want.
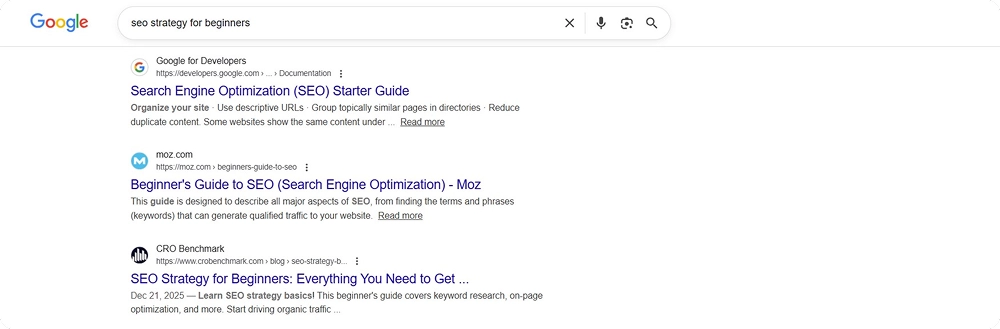
As you can see from the example above, the search intent for “SEO strategy for beginners” is mostly informational, as the search results are blog posts or guides on effective SEO strategies.
You can also use various SEO tools that can help you with the identification of search intent. Let’s take Ahrefs, one of such tools, as an example.
Step 1: Go to Ahrefs.
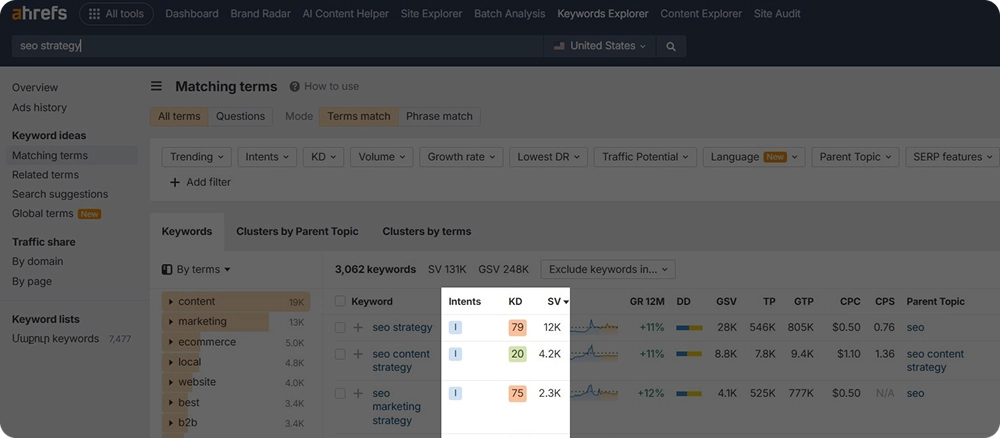
Step 2: In the Keyword Explorer section, just enter your keywords, and there you go: you will see all the matching and related keywords with their search intents.
2. Identify Target Keywords
While you start with one main keyword, SERP analysis shows the bigger keyword picture around your topic.
This process begins right from the first step of your analysis: typing the focus keyword. When you type your keyword in the search box, see what keyword suggestions also appear. These are usually longer keyword options that people also search for.
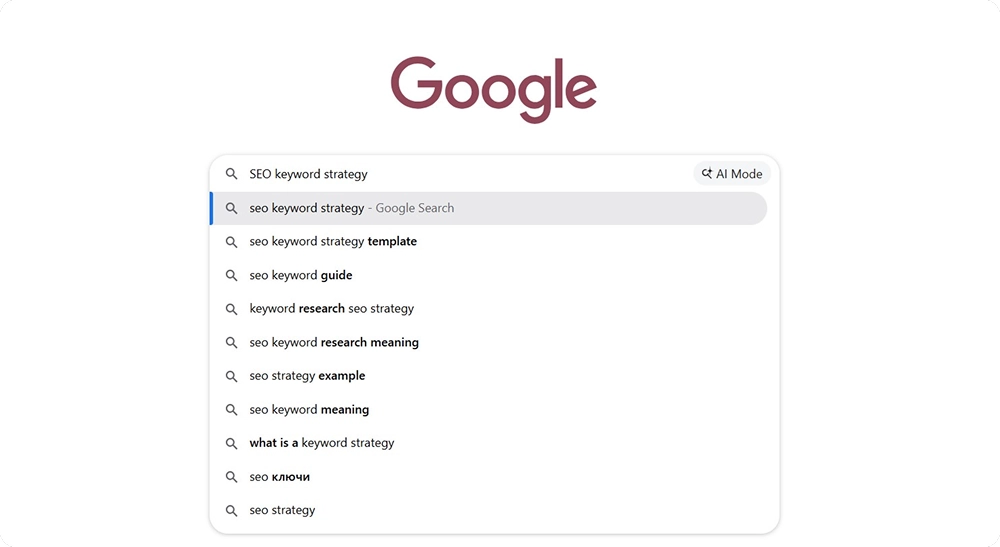
When looking at the SERP, notice how top-ranking pages phrase the main topic differently. This shows you alternative ways to approach the same subject that Google values.
Check the People also ask and Related searches sections for similar terms. These related keywords show what users are actually searching for when they explore this topic.
Here’s what the section looks like:
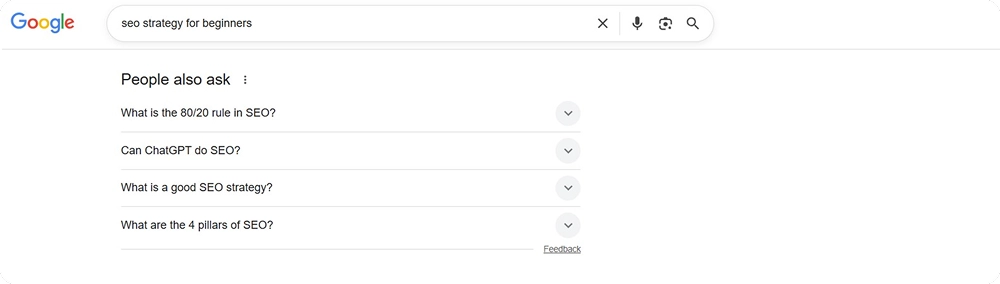
Look for long-tail keyword opportunities by finding longer, more specific phrases in titles and headings of ranking pages. These targeted phrases are often easier to rank for while still bringing in good traffic.
Watch for keyword metric signs: keyword difficulty and search volume, especially. If major authority sites fill all top positions, the keyword may be very competitive. Understanding this helps you set realistic goals.
Again, these metric insights are also presented through professional SEO tools.

Pay attention to how often the keyword shows up in top-ranking titles, URLs, and snippets. This shows you what’s expected without overdoing it.
3. Analyze Competitors and Top Content
The top-ranking pages, your SERP competitors, are your live guides for what’s currently working. Study them carefully.
Here, the key elements for you to check are:
-
- Content depth and length: Are the top results long guides (2,000+ words) or short answers?
- Content format: Articles, videos, infographics, product pages, or lists?
- Content quality: How well do they cover the topic? What special value do they offer?
- Domain authority: Are results filled with major brands, or is there variety?
- Freshness: Are the top results recently published or updated?
- Engagement signals: Look at social shares, comments, and visible interaction numbers
- Content structure: How do they organize information? What headings and subheadings do they use?
- Keywords used: With competitor keyword tracking, identify what keywords your competitors used to rank for and how.
This competitive information shows you the standard you need to meet or beat to rank well.
4.Assess SERP Features
Modern SERPs include much more than just ten blue links. They also include important features that can really impact click-through rates and visibility.
Common SERP features to identify:
- Featured snippets: The boxed answer at the top of the search results (paragraph, list, table, or video)
- AI overview: A quick answer box that includes summarized answers generated from multiple sources.
- People Also Ask (PAA): Additional questions related to the search
- Local pack: Map results with local business listings
- Knowledge panel: Information box appearing on the right side about entities (people, places, organizations)
- Image pack: Row of related images
- Video carousel: Featured video results, often from YouTube
- Shopping results: Product listings with prices and images
- Site links: Extra links under a main result
- Reviews and ratings: Star ratings visible in results
Why this matters: If a featured snippet or an AI overview exists, you can optimize to capture it. If video results appear, you might need video content. If there’s a local pack, local SEO becomes important. Understanding which features appear helps you decide what content formats to create.
5. Spot Content Gaps and Opportunities
This is where you find your edge by identifying what’s missing or poorly covered in current results.
Here are some tactics you can use to identify content gaps:
- Start by asking what subtopics top results ignore or mention only briefly. Look closely at whether user questions in PAA sections or forums aren’t fully answered by ranking content. These unanswered questions show clear gaps you can fill.
- Consider if you could provide more current data or examples than the existing content. Maybe there’s a different angle or view not represented in the top results. Sometimes, all ranking pages approach a topic the same way, leaving space for a fresh take.
- Finally, check if you could improve on the user experience, readability, or visual presentation. Look for weaknesses in top content, such as outdated information, a lack of examples, poor formatting, missing visuals, or incomplete coverage.
Understanding where your SERP competitors are lagging behind is essential, as their content gaps are your chance to create something truly better.
Best Tools for Your SERP Analysis
Of course, you are not alone in your SERP analysis journey. There are various tools that can help you with all the necessary SERP analysis processes.
Below are the most common ones:
Google Search Console

A free tool from Google that shows how your site performs in search results. It’s essential for understanding how Google sees your site and tracking your current performance.
Key features:
- Shows which keywords bring traffic to your site
- Reveals your average ranking position and click-through rates
- Spots technical issues affecting visibility
Semrush
An all-in-one SEO platform with strong SERP analysis features. It’s particularly useful for competitive analysis and discovering new keyword opportunities.
Key features:
- Tracks keyword rankings and analyzes competitor strategies
- Shows SERP features and keyword difficulty scores
- Reveals what content ranks for your target keywords
Ahrefs
Ahrefs is known for its large backlink database and excellent keyword research capabilities. It helps you understand why pages rank and what you need to do to compete.
Key features:
- Shows who ranks for any keyword with traffic estimates
- Excels at competitor analysis and backlink research
- Explores related keyword ideas and ranking opportunities
To Wrap up
Even with great content, solid keyword research, and optimized SEO methods, reaching the top of Google rankings is not guaranteed.
Understanding what SERP analysis is and including it in your content strategy is crucial. Track your competitors, identify content gaps, and examine the results closely. You will notice your content gradually rising in the rankings.
By understanding what works in your industry, you can create more focused, engaging content that meets user needs and stands out in search results.