If you’ve been into SEO, you’ve probably heard about nofollow links. At first, they seem simple enough, but the more you read, the more confusing they get. Do nofollow links help SEO? Should you even care about them?
The truth is, it’s not as clear-cut as it used to be. Some people say they’re worthless, while others argue they still matter.
In this article, we’ll break down how nofollow links actually work today and whether they’re worth your attention. By the end, you’ll understand what changed, why it happened, and how to think about nofollow links in your SEO strategy.
What are NoFollow Links?
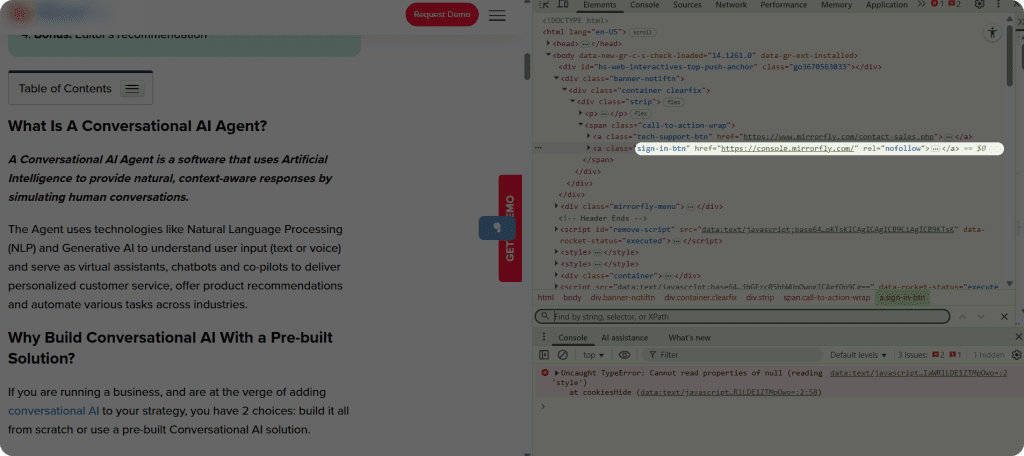
Nofollow links are HTML hyperlinks that include a special [rel = “nofollow”] attribute, which tells search engines not to pass SEO value, also known as the “link juice” to the destination page. This is a way of protecting the page rankings from worthless or spammy links.
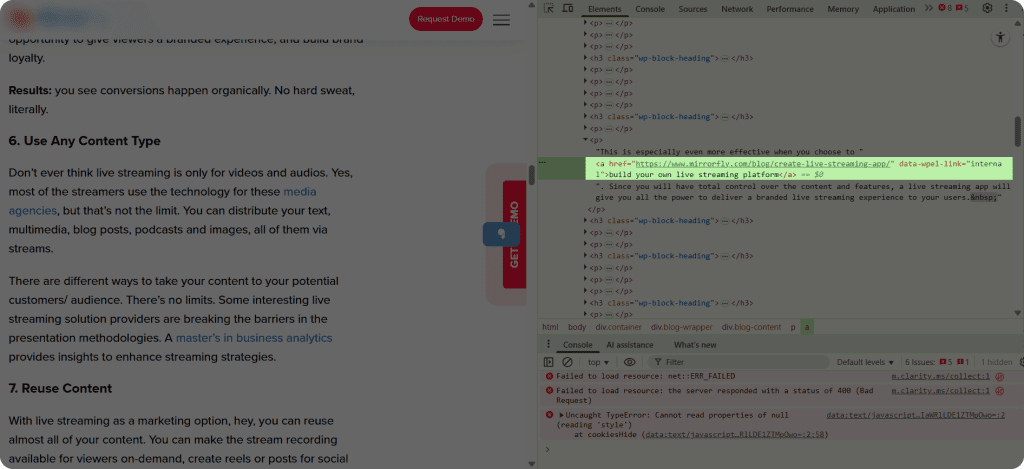
The opposite of nofollow links are the dofollow links, which simply do not have any attributes. These kinds of links are automatically eligible for ranking and transfer the link juice. Therefore, if you do not add a nofollow attribute to your links, they will be considered as regular and affect your rankings.
Below is an example of a dofollow link:
And here is an example of a code with the nofollow attribute:
They were introduced by Google in 2005 to fight the spam comments under blog posts. Many spammers would leave links to their websites in the comments or in forum posts that would harm the reputation of that website. Therefore, the nofollow attribute is being added to make certain links worthless and not eligible for ranking.
For a long time, this was used to fight spammy links in the comments, forums, or paid advertisements that the site owners weren’t able to control. However, this attribute started to also be used to fight the paid links, as per Google’s guidelines, purchased links were prohibited from affecting the page rankings. The websites that would purchase links to get rankings would simply receive penalties and lose their rankings.
By default, regular links without this attribute are considered dofollow, without any need to add a special attribute to the HTML code.
Types of NoFollow Links
Alongside this change, Google introduced two more link attributes to better explain to Google why site owners do not want the links to be considered for ranking, and make search engines better understand the nature of different links across the web.
The “SPONSORED” Links
The sponsored attribute represents a signal in how search engines want webmasters to identify commercial relationships in links. It’s pretty straightforward: if someone has paid you to include a link on your site, whether that’s through a direct payment, a free product, or any other form of compensation, you’re supposed to tag it with rel=”sponsored”.
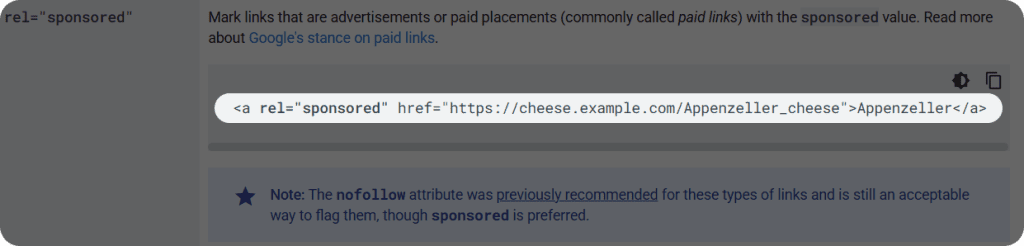
The whole point is transparency. Google doesn’t want people to trick the system by buying their way to the top of search results through paid links. They had always had rules against this, but before 2019, everyone simply used the generic nofollow tag for everything. Now with the sponsored attribute, you’re being more specific about why you’re marking the link, which helps Google understand the web better.
For example, if you’re a tech blogger and Samsung sends you a free phone to review and you link to their site, that should be marked as sponsored. The same goes for affiliate links, where you earn commission on sales.
The “UGC” Attribute
The rel=”ugc nofollow” attribute, which stands for user-generated content, is designed for links that appear in content created by users rather than the site owner or editorial team. This includes comments on blog posts, forum discussions, user profile pages, product reviews, and any other area where visitors can contribute content that may include hyperlinks.
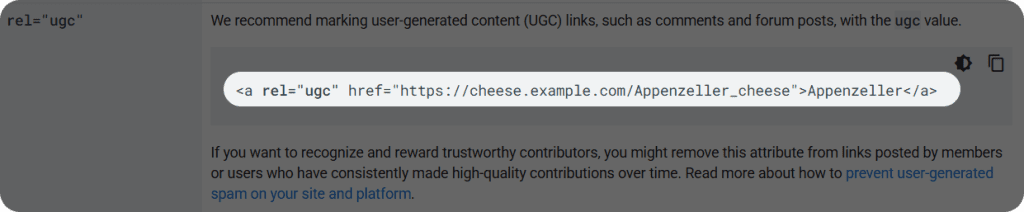
When you publish content on your own site, you care for the quality and relevance of any links you include. However, when you allow user contributions, you lose direct control over what gets posted. A site with an active comment section might receive dozens or hundreds of comments daily, making it impractical to manually review every link before it goes live. The ugc attribute signals to search engines that these links come from third parties and shouldn’t be treated with the same level of trust as editorial links.
UGC links can be found in։
- Comment sections and forums
- User profiles on social networks
- Q&A sites like Stack Overflow or Quora
- Wiki-style collaborative documents
- Marketplace listings
Essentially, if a user who isn’t part of your organization can add or edit a link without going through an editorial approval process, it should be tagged as ugc.
Do Nofollow Links Still Matter for SEO?
Nofollow links are a bit complicated when it comes to SEO. The simple answer is yes, they still matter, but not in the obvious way that regular links do. Their value has changed a lot since Google updated its rules in 2019. Therefore, the real question is, do nofollow links help SEO somehow, or just cause harm if left unfixed?
In the past, it was simple: nofollow links gave you zero SEO value. They were basically invisible when search engines calculated rankings. This made sense when nofollow was a strict rule that Google had to follow.
Now Google can choose to ignore the nofollow tag in some situations. They haven’t told us exactly when they do this, which is normal for Google since they don’t want people to game the system. However, you shouldn’t plan your SEO around getting nofollow links and hoping Google will count them. In most cases, they probably don’t help your rankings directly. But they do offer other real benefits that can help your SEO in indirect ways:
They Bring Direct Traffic
The most obvious benefit is actual visitors. A nofollow link from a popular website can send thousands of people to your site, whether it helps your rankings or not. If someone reads an article that links to you, they’ll click on it either way. This traffic can lead to sales, brand awareness, and possibly even natural backlinks if those visitors have their own websites or social media accounts.
They Make Your Link Profile Look Natural
Real websites naturally get a mix of nofollow and dofollow links. If your website only has dofollow links, it might look suspicious to search engines. Normal sites get nofollow links from social media, comments they leave on other blogs, news coverage, and other sources. Having only dofollow links can make Google take a closer look at whether you’re doing something shady.
They Build Brand Recognition
Nofollow links help people recognize and trust your brand, even if they don’t directly boost your rankings. When your brand gets mentioned and linked around the web, it builds awareness. This influences how people behave in ways that eventually affect SEO, like searching for your brand name more often or clicking your site in search results because they recognize you.
They Help Search Engines Find Your Content
There’s also a case that nofollow links help with getting your pages discovered and indexed, even if they don’t help rankings. While Google says they usually won’t follow nofollow links for crawling, there are exceptions. New websites might benefit from any links that help search engines find their content. Plus, search engines still read the text around a nofollow link, so they can understand what topics your site is relevant to.
The Bottom Line
For practical SEO work, focus mainly on earning valuable dofollow links from relevant, trusted sources. But don’t turn down nofollow link opportunities that offer other clear benefits like traffic, visibility, or building relationships.
Your link building should prioritize quality and relevance over quantity and link types. One dofollow link from a highly relevant, authoritative site in your field is worth more than dozens of nofollow links from random sources. But it’s also worth more than dozens of low-quality dofollow links from spammy directories.